|
SSADM
- Stage O
|
|
Feasibility Module
|
Page
Contents
Introduction
- In this stage an assessment of the proposed IS is carried out to determine
if the system can meet the business requirements it is intended to meet.
- At the end of the Feasibility Module, it should be possible to determine
whether a full SSADM study should be undertaken.
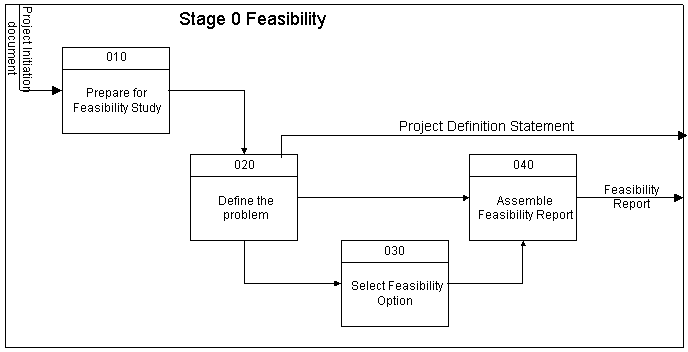
As we can see in the figure above there are four steps in this stage, namely
- 010 Prepare for the Study
- 020 Define the Problem
- 030 Identify Feasibility Options
- 040 Assemble Feasibility Report
Step 010 Prepare for the Feasibility Study
This step is broken into two major tasks:-
|
Tasks
|
Description
|
| 10 |
- Review the Project Initiation Document (PID) and relevant background
material. Assess the scope and complexity of the proposed IS.
- Create a Context Diagram, current Level 1 DFD and Overview
Logical Data Structure.
- Identify the base requirements from the PID and enter them in the
Requirements Catalogue. Report errors and inconsistencies
in the PID.
|
| 20 |
- Identify the stakeholders for the business areas concerned.
Establish how they are involved and brief the User representatives.
- Identify those areas to be investigated and define the methods
to be used.
- Agree the Feasibility Study scope with the project board.
|
Techniques used in Step 010 are:
- Data Flow Modelling
- Logical Data Modelling
- Requirements Definition
Step 020 Define the Problem
Here we carry out more detailed investigation of the business and its information
needs. Users of the system are defined, the new services wanted from the system
and any problems associated with the current services and operations.
|
Tasks
|
Description
|
| 10 |
- Identify the activities and information in the area of study
that are necessary for the business unit to meet its objectives.
- Draw a Level 1 DFD for the required environment. Amend the
Overview LDS to include entities and accesses in the required
environment.
|
| 20 |
- Investigate the current environment. If necessary, expand
DFD to Level 2.
- Identify, with the Users help, those aspects of the current
operations where improvement or change is required. Enter these
in the Requirements Catalogue.
|
| 30 |
- Define the Users of the new system in the User Catalogue.
|
| 40 |
- Identify with the Users new features in the required system (i.e.
new processes). Record these in the Requirements Catalogue.
- Identify any non-functional requirements (i.e. service levels,
response times, recovery and security). Record these in the
Requirements Catalogue.
|
| 50 |
- Prepare a Problem Definition Statement to summarize the requirements
and assess priorities for the business objectives.
|
| 60 |
- Agree the Problem Definition Statement with the Project Board.
|
Step 030 Select Feasibility Options
Here a set of options for solutions are developed to the problems
identified and agreed. The options are presented to the Project Board, for the
selection of one which will define the way forward. The selected option will
define one or more projects to meet the requirements of the target business
area.
The options combine both business option elements, to define
the scope of the project and technical options, to describe the physical environment
in which it will operate.
After the board makes its selection, development plans are
produced, in outline for associated projects.
Tasks Description
|
Tasks
|
Description
|
| 10 |
- Draw up a list of the minimum requirements for the new system, both
functional and non-functional. All options must satisfy these
basic requirements.
|
| 20 |
- Define up to six Business System Options, which will satisfy a range
of requirements, from the basic minimum to all listed.
|
| 30 |
- Define a list of outline Technical Systems Options, to represent a
full range of technical solutions. Each technical solution should
satisfy the constraints and requirements of at least one Business
System Option. In consultation with the Users, draw up a list
of up to six composite Business and Technical Systems Options.
Reduce these to a short list of about three.
|
| 40 |
- Describe in prose, each short-listed option. This description can
be supported by DFDs and an LDM. To illustrate the differences
between them. They should be supported also by outline Cost/Benefit
Analysis and Impact Analysis.
|
| 50 |
- Identify the preferred option. Produce an outline development
plan for each recommended project.
|
| 60 |
- Present the short-listed options to the project board, and other User
audiences.
- Assist in the selection of the one chosen option, with explanation
and clarification of the implications of each. Record any decisions
made, with reasons.
|
| 70 |
- Develop an Action Plan for each selected project(s). This should include
a description of the technical approach, and outline development
plans.
|
Techniques used in this step include:
- Business Systems Options
- Technical Systems Options
- Data Flow Modelling
- Logical Data Modelling
Step 040 Assemble the Feasibility Report
In this step the Feasibility Report is published (after checking by Quality
Control).
|
Tasks
|
Description
|
| 10 |
- Check the completeness and consistency of the Feasibility Study Module
by reviewing the products above. Amend the products as a result
of reviews, if necessary or appropriate.
|
| 20 |
- Assemble and publish the Feasibility Report Documents.
|
Summary
- Feasibility is an activity that should ideally be carried out for all but
low risk projects. It is a decision point; possible decisions include the
option to terminate the project.
- On completion of this module, if approved by the Project board, we move
into the first Module of SSADM proper, Requirements Analysis.

